「数据仓库技能树」--Hive Tuning
what and why
Tuning: 逻辑正确,但实现消耗的资源超出预期。
资源: 任务运行时间, 占用集群的计算资源(Memory&Cores)
解决问题,促使Tuning的契机 ——
对现行任务,虽然能顺利执行成功,但对效果希望进行改善。
当和内行人交流Hive Tuning(也是很多大数据-数据仓库岗位时会聊的一个话题),至少胸中要懂的一些场景和策略,不要眉毛胡子一把说,没有章法。
业务逻辑,如果这个任务不是自己是第一手的开发者,那么半路介入,需要先了解业务背景。
SQL语句的框架,细节有无优化空间。
输入信息: 任务执行日志,查询计划详情
嗅探点:
源数据(source) 表的格式, 比如orc 是有提升的
加载数据规模;
扫描分区个数;
元数据MySQL 负载状况(HiveServer2 Performance)
执行任务个数,单个任务消耗时间
使用的权限&锁,引起的问题
内存管理, Java堆内存
当多人操作同一数据时,可能会看到A在注入(修改)数据,B在写入数据。
概率较低, 看日志根据关键字定位。
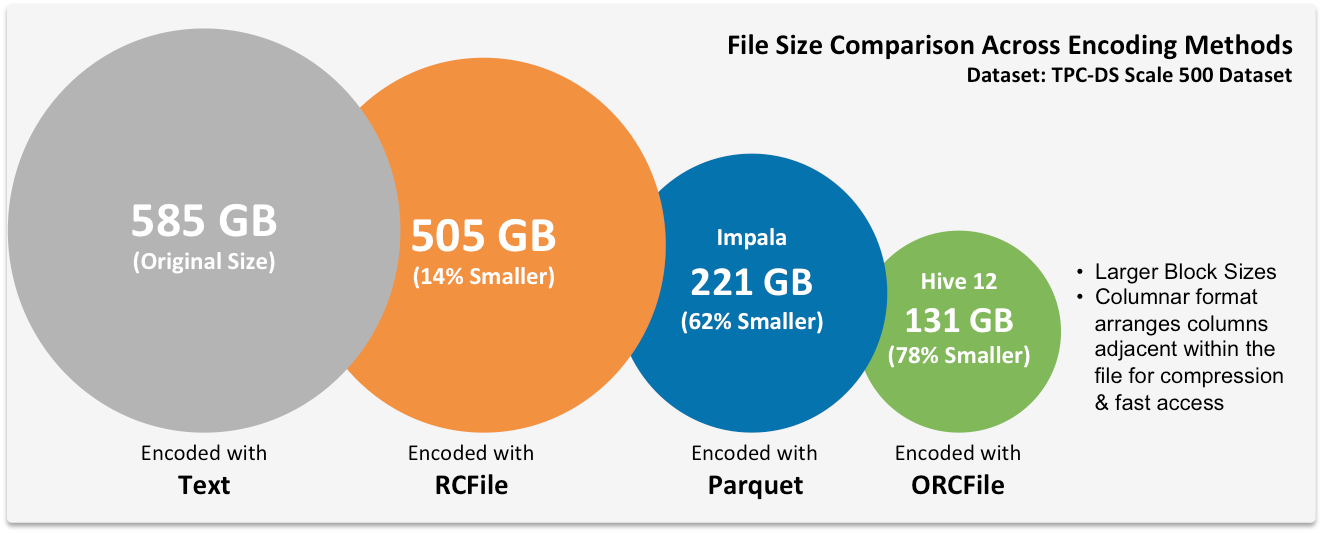
语句分析
减少和业务需求无关的不必要操作, 例如没必要的全局排序:
order by vs. sort by
避免使用order By, Order By 会使用一个全局Reducer进行整体排序 —— cause a performance bottleneck, setting the number of reducers to one, making it very inefficient for large datasets.
人工列剪裁
减少不必要的列扫描, 即不要使用 select *
人工谓词下推
先filter 再join
开启Map端聚合参数
Group By
分析执行计划
-
cost-based-optimizer (CBO)
CBO可以给出 joins的执行顺序、并行度,量化执行任务的开销。
设置参数:set hive.cbo.enable=true; -
query vectorization
参数: hive.vectorized.execution.enabled 设置为true
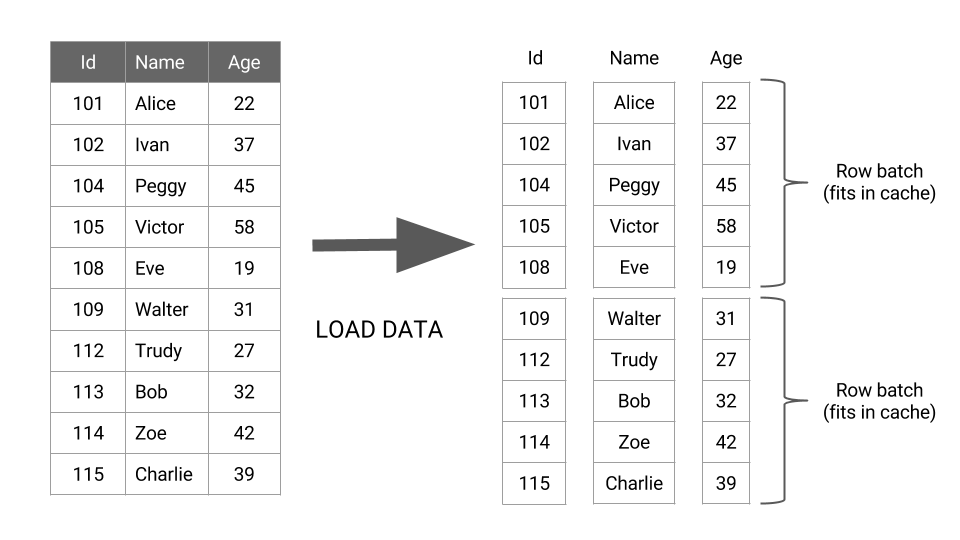
https://docs.cloudera.com/documentation/enterprise/6/6.3/topics/hive_query_vectorization.html#enabling_hive_query_vectorization
内存与Reducer个数优化
set hive.exec.reducers.max=8;
set mapred.reduce.tasks=8;
Join细节
大表与大表的join 之 空Key
如果某个join条件中引入了 这个空Key
处理方式, 分析业务是否能过滤掉空值,如果不能过滤,将Null 修饰为一个有效值, 或者随机值。
**要特别注意的是, 这个随机值不能与第二个表发生真实join, 否则产生错误结果。 **
-- 原sql
select count(a.uid) from A left join B on A.uid = B.uid2
-- 过滤空值
select count(a.uid) from ( select uid from A where uid is not null ) A
left join B on A.uid = B.uid2
-- 随机join
select count(a.uid) from A
left join B on nvl(A.uid, rand()) = B.uid2
join 时的倾斜问题 + groupby 倾斜
SET hive.optimize.skewjoin=true; --If there is data skew in join, set it to true. Default is false.
SET hive.skewjoin.key=100000; --This is the default value. If the number of key is bigger than this, the new keys will send to the other unused reducers.
groupby 时的倾斜
set hive.groupby.skewindata= false; (默认 false) 开启 true 将会实现负载均衡, 多开启 map 任务.
大表的 distinct 操作
count(distinct xx) 使用一个 reducer 计算l 等效的操作是 group by xx 再 count 但对 reducer 要求来说是不同的.
强制指定 reducer 数量 : set reducer.num
大表与小表的join 之 mapjoin
map join
自动开启 hive.auto.convert.join 默认是true
看执行计划, 如果设置了该参数, 在计划中会出现一个 “Map Local Tables” —— 将小表作为本地缓存。 如果不设置, 小表是正常的MapReduce Stage。
大表小表的顺序是没有关系的。
对于大表与小表的Join能否使用 mapjoin, Hive默认大小25MB修改。
0: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000/> set hive.mapjoin.smalltable.filesize;
set
hive.mapjoin.smalltable.filesize=25000000
这里 join是默认的inner join, 如果是left join 则要注意了。
left join , map join不会生效。
Stage整体
- 提升并行度
set hive.vectorized.execution.enabled=true;
set hive.exec.parallel=true;
set hive.exec.parallel.thread.number=8;
如果查询无依赖的,可以转为并行运行。
如果集群当前的利用率已经很高,开这个参数提效果不明显。
参考资料: